Die-casting mold is an important process equipment in die-casting production. It plays an extremely important role in the smooth progress of production and the quality of castings. It interacts with and restricts each other with die-casting production process and production operations.
Composition of Die Casting Mold
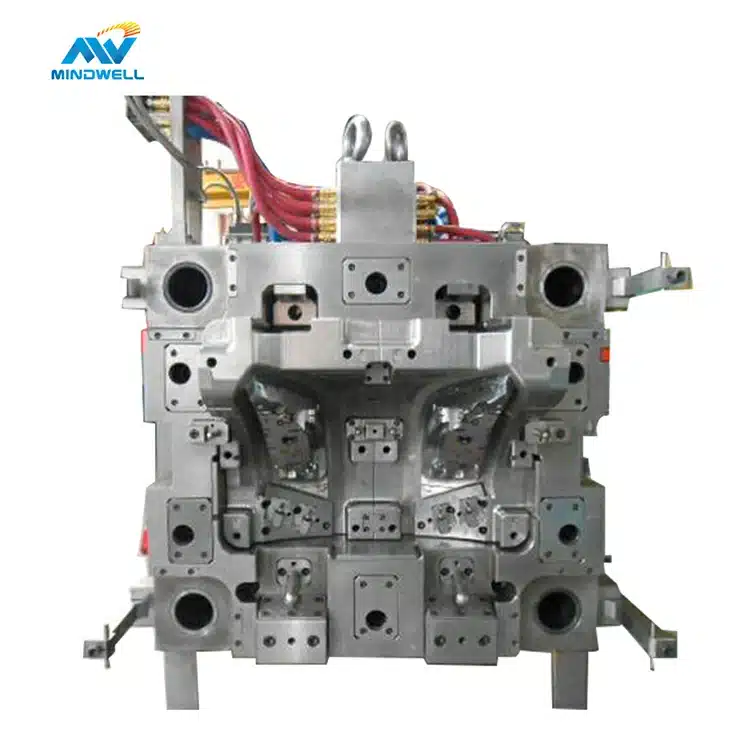
Die-casting mold is composed of two main parts: fixed mold and moving mold.
- The fixed mold is fixed on the fixed mold seat on one side of the pressure chamber of the die-casting machine. It is the side where the metal hydraulic pressure enters the cavity of the die-casting mold, and also includes part of the cavity of the die-casting mold. There is a sprue on the fixed mold that directly connects with the die-casting machine Pressure chamber or nozzle connected;
- The movable mold is fixed on the movable mold base of the die-casting machine, and is separated and closed with the fixed mold as the movable mold base moves. For molds that require a core-pulling mechanism, the core-pulling and casting ejection mechanisms are usually also set on the moving mold Inside. And follow the movable mold installation plate to open and close the mold. When the mold is closed, the cavity and the casting system are closed, and the liquid metal is filled with the cavity under high pressure. The ejection mechanism pushes the casting out.
The basic structure of the die casting mold
A set of molds usually consists of the following components:
- Forming parts (moving and fixed mold cores, molding inserts, core pulling cores, etc.)
- Mold base part (moving and fixed mold splints, AB boards, trays, mold feet)
- Winding system (runner group, splitter cone, cross runner, inlet runner)
- Overflow system (overflow trough, steam discharge trough)
- Ejector mechanism (thimble, ejector pin fixing plate, ejector plate, reset lever)
- Guide components (guide post, guide bush, center guide post, center guide bush)
- Core-pulling mechanism (core-pulling slider, slanted guide post, tight block, spring, etc.)
- Others (cooling system, heating system, reinforced columns, etc.)
What material is the die-casting mold made of?
- The die-casting molds of our company mainly use the following steel materials:
- H13 (heat-resistant steel) is used for front and rear mold cores, core-pulling cores, sprue sleeves, and diverter cones.
- 45# steel (for A, B plate, slide rail, inclined guide post, etc.)
- T8, T10 (guide column, guide sleeve, thimble, reset rod, etc.)
- A3 steel (front and rear closing templates, pallets, ejector plates, mold feet, etc.)
Die Casting Die Design
- The common materials used for die-casting molds are zinc alloy and aluminum alloy. Zinc alloy is generally hot chamber die-casting, the temperature is about 450 degrees, hot chamber die-casting, there is a crucible, and the remaining material can be sucked back. The aluminum alloy is die cast in a cold chamber at about 600-700 degrees. For cold chamber die-casting, pour a certain amount into the mold and press it down with a punch. The cold chamber is mostly a vertical die-casting machine. The flow of molten metal, the upper layer is faster than the lower layer, and finally the whole is forward, sprayed in a mist. The zinc alloy die-casting mold and the plastic mold have more parts in common. The aluminum alloy mold can press zinc alloy, but the zinc alloy mold cannot press aluminum alloy. Shrinkage zinc alloy is generally 0.5%, aluminum alloy is generally 0.6%.
- The mold bases of the die-casting molds are all CH-type, CI can not be used, and the guide posts are generally arranged on the front mold, and the template is a little thicker than the plastic mold. The reset rod cannot be spring loaded.
- The core steel of the mold is H13, SKD61 or 8407, and the heat treatment is generally HRC48-52, which is basically the same as that of plastic molds.
- Generally, the layout is symmetrical when arranging, and the water is generally eccentrically injected from the side during cold pressing, and the product is at least 40MM from the edge of the die.
- The splitter cone is generally about 30 degrees higher, with a slope of 5 degrees on one side. The standard size is generally 50 in diameter.
- The trapezoidal cross channel is generally 20-30 wide, 8-10 deep, unilateral slope 15-20 degrees, and the bottom is inverted R2-3. Generally, it is opened on the back mold, and it can be opened on the front mold when the four sides are in position. The cross runner is generally equipped with a blind runner, which is not allowed to go straight to the core, and the glue is fed tangentially. The commonly used ones are fan-shaped, T-shaped, and comb-shaped. They are often made of technological steps, with the purpose of changing the speed and improving quality.
- The flow path of zinc alloy is equivalent to that of plastic molds. Generally, 6-7 openings is almost enough. If there is a slope of 5-10 degrees, 3-4 small molds are enough. The sprue sleeve of zinc alloy is placed directly on the front mold core, instead of being placed on the parting surface like aluminum alloy. The splitter cone is much longer than that of aluminum alloy, and the single side is also 5 degrees.
- The distance between the inner gate and the product is generally 1.5-2.0. The connection method with the cross-flow channel is the same as that of the plastic mold. It can directly enter the water, or it can be lapped into the water. The slag bag is opened at the end of the molten metal flow and the place where gas may be trapped. To prevent backflow, generally it should not be too large, and the thickness is smaller than the ingate. Only one overflow port is opened to make a secondary slag bag. Make scumbags. Exhaust is mostly done on the parting surface, usually behind the slag bag, with a depth of 8-25MM wide and below .0.1. It is not straight and needs to be turned.
- For the surface that needs secondary processing, the allowance is generally 0.3-0.8, and an extra 0.5 is taken.
- The inclination of die-casting products must have a minimum of 1 degree, and a minimum of 2 degrees for the forming hole.
- Die-casting molds do not generally have inner sliders, inclined tops, and cylinder ejections. The inner buckle is processed by secondary processing to ensure the accuracy.
- The cooling water is generally 20-25 from the product, at least 15. Otherwise, there will be water marks on the product.
- Die-casting molds must first consider the difficulty of forming and the places with thick walls, and fill them first to avoid direct impact on small cores. The reason why the comb-shaped gate is better than the large-area fan-shaped gate is that it is not easy to shrink and lose meat here, and the gate is easy to remove.
- When inserting small needles in the back mold, the root is generally chamfered with C angle or R angle to strengthen the strength.

Unser Vorteil
Mindwell is a professional custom die-casting service company. Our company has advanced die-casting mold precision machine tools, which can better ensure the dimensional accuracy of the mold. Our company has experienced senior mold technicians. The rich experience of the technicians is the guarantee of the practicality of the die-casting mold. Good mold design and manufacturing are the basis for the long life, low failure and high efficiency of the die-casting mold.
In addition to experienced engineers and equipment, our company has been focusing on the die-casting industry for many years. We have close relationships with material suppliers and heat treatment plants. We have set up special departments in quality management and after-sales service systems to ensure that customers get high-quality die-casting products. Both molds and die castings are of high quality and high efficiency.