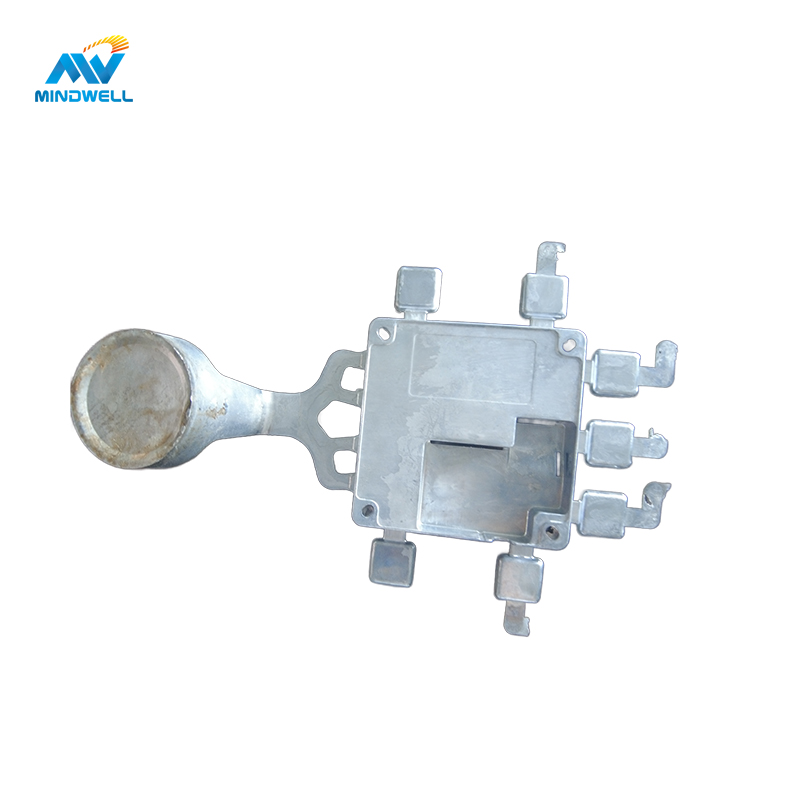
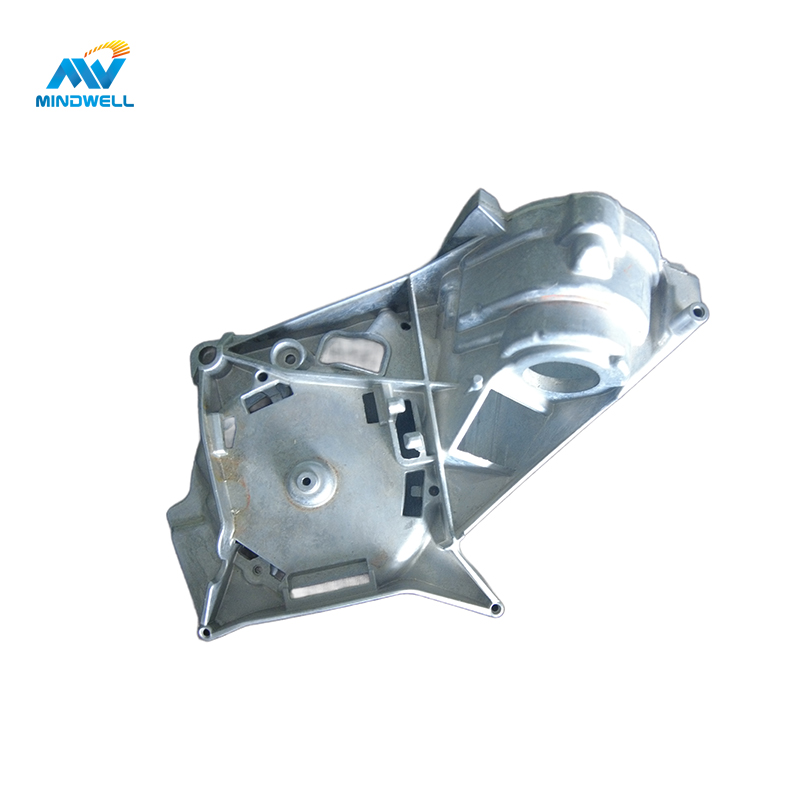
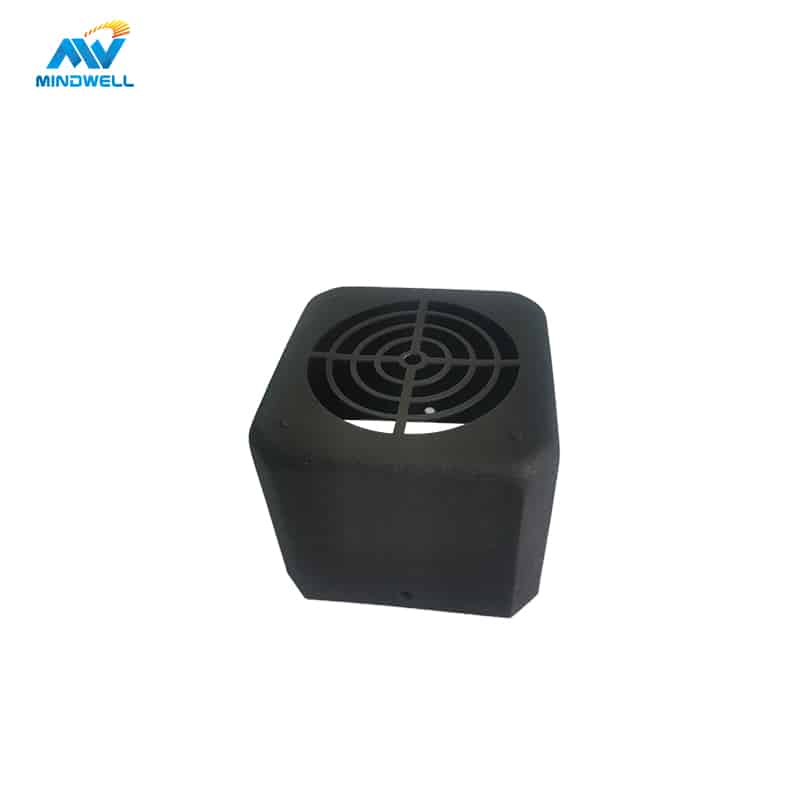
Aluminum die-casting is a process in which aluminum alloy is heated to a liquid state and injected into a die-casting mold for cooling and forming. The process offers advantages such as cost reduction, precision, efficiency and large-scale manufacturing. Its material utilization rate is high, and the blank utilization rate is as high as 90%, reducing costs. Applications include the industri otomotif, electronics, household appliances, construction and decoration, aerospace, military, and general machinery. Aluminum die castings have excellent compatibility, good surface roughness and high dimensional accuracy.
Pendahuluan
Aluminum die-casting is a process in which aluminum alloy is heated to a liquid state and then injected into a die-casting mold to be cooled and formed. Aluminum die-casting offers many advantages, including cost reduction, precision, efficiency, and large-scale manufacturing. Its material utilization rate is high, and the blank utilization rate is as high as 90%, reducing costs.

The definition and importance of aluminum die casting
The method of die-casting aluminium involves heating an aluminium alloy to a liquid condition and then injecting it into a die-casting mould, where it cools and solidifies. The benefits of aluminium die-casting over other production techniques are high material utilisation, high productivity, and high product accuracy. Aluminium die-casting is another name for aluminium die-cast items. There are several uses for aluminium die-casting, including as the production of equipment, electronics, and automobile components. Aluminium die-cast components are lightweight, strong, and resistant to corrosion, all of which may significantly increase an automobile’s performance and fuel efficiency. Aluminium die-cast components offer strong mechanical properties and high heat conductivity, which helps prolong the product’s life and stability. Aluminium die-cast parts are high-quality and dependable components used in machinery manufacture that may extend equipment life and performance. As a result, aluminium die-casting has been extensively developed and employed in a variety of industries. As new materials are created and contemporary manufacturing technology continues to gain popularity, aluminium die-casting’s application possibilities will expand.
Application areas of aluminum die casting
The aluminum die-casting process is used in many fields. These are a few of the major domains:
- Automotive industry: Engine parts, brakes, steering gears, and other components are among the many products in the automotive industry that employ aluminium die-casting technology. Aluminium alloy’s strength, light weight, and thermal conductivity allow it to satisfy energy-efficient and lightweight vehicle requirements.
- Electronic and communication equipment: Components for electronic and communication equipment, such casings, radiators, connections and sockets, etc., are made using the aluminium die-casting method. Due to its strong electromagnetic shielding and thermal conductivity, aluminium alloy may enhance the equipment’s stability and performance.
- Home appliances: The field of home appliances and electrical equipment, including air conditioner casings, washing machine drums, refrigerator components and TV brackets, is another area in which aluminium die-casting technique is extensively used. Products made of aluminium alloy may have their texture and aesthetics enhanced by their surface quality and appearance.
- Construction and decorating sector: Window frames, door and window accessories, interior decoration elements, and other items are manufactured using the aluminium die-casting method in this sector. In the domains of building and decorating, aluminium alloy may satisfy criteria for material strength, corrosion resistance, and attractiveness as it is lightweight, weather-resistant, and malleable.
- Other areas: The aerospace, military, general machinery, and other fields also make extensive use of aluminium die-casting technology. For instance, aluminium die-casting may be used to produce propellers, engine parts, aircraft shells, and other components. Additionally, a variety of components for general mechanical equipment, including machine tool parts, pump bodies, valves, pressure vessels, etc., may be made using the aluminium die-casting technique.
Advantages and limitations of aluminum die casting
Die-casting aluminium has the benefits of being inexpensive, very precise, efficient, and capable of producing complicated forms. But there are also some restrictions that, depending on the application, must be carefully taken into account.
Benefits of die casting aluminium:
- The molten metal retains great fluidity under high pressure and high speed, enabling the manufacturing of deep hollow metal objects with complicated geometries, clear outlines, and thin walls.
- Die castings made of aluminium exhibit excellent compatibility, good surface roughness, and great dimensional precision.
- Costs may be reduced because of the high material utilisation rate and 90% blank utilisation rate.
- Excellent productivity and appropriate for large-scale manufacturing.
- Inlays may be utilised to suit specific performance needs and are simple to employ.
- inexpensive. Aluminium die-casting may lower production costs and offers a simpler manufacturing process than conventional manufacturing techniques.
- It is capable of producing vast volumes of metal castings and is extremely repeatable.
- Because of its great strength, the material is able to tolerate stress in situations with high loads and high temperatures.
- The surface is simple to work with and paint, and coating may improve its attractiveness, resistance to corrosion, and durability.
Aluminium die casting does, however, have several drawbacks.
- Die castings are not appropriate for small batch manufacturing because they often have holes and oxidised impurities.
- Both the kinds of die casting alloys and the sizes of die cast items are restricted.
- Costly and requiring a significant investment are the moulds and equipment.
- During the manufacturing process, waste materials and exhaust gas will be produced; these items need to be treated for environmental protection.
- The majority of aluminium die-cast components are thin and brittle.
- Aluminium die casting may not be the ideal option for applications requiring a high level of strength and rigidity.
Raw material preparation
Selection and quality control of aluminum ingots
Ensuring the quality of aluminium die-casting products requires a number of preliminaries, including the selection of high-quality ingots that satisfy the specifications and rigorous quality control. To guarantee the quality and functionality of the finished product, it is also vital to pay attention to other elements of the aluminium die-casting process, such as mould design, die-casting parameter settings, post-processing procedures, etc.
The following elements should be taken into account while selecting aluminium ingots:
- Aluminium content: To guarantee the quality and purity of the raw materials, aluminium ingots should have a minimum of 99.5% aluminium content.
- Impurity content: Aluminium ingots’ impurity content should adhere to all applicable national regulations. To prevent negative impacts on die casting performance, the content of impurity elements like iron, silicon, copper, etc., should be kept within a certain range.
- The aluminium ingot should have a regular rectangular parallelepiped shape and be free of any visible faults in terms of distortion or deformation. There should be no flaws like pores, fissures, or slag inclusions; the surface should be smooth and level.
- Dimensional specifications: The length, breadth, and height of aluminium ingots must fulfil contract specifications or applicable national standards. The dimensional accuracy of the ingots must also meet the criteria to guarantee the stability and dimensional accuracy of die castings.
- Raw material quality certificate: To guarantee the quality, traceability, and dependability of the raw materials, aluminium ingots with this certificate should be used.
The following tasks must be completed for aluminium ingot quality control:
- Inspection of incoming material: Verify that aluminium ingots entering the plant meet all criteria by conducting a quality inspection that covers things like appearance quality, dimensional standards, chemical composition, etc.
- Process inspection: To make sure the die-casting parts match the specifications, they are randomly or thoroughly examined during the die-casting process to verify the parts’ appearance quality, dimensional correctness, chemical composition, etc.
- Handling of unqualified products: Track down and manage unqualified die-casting parts or aluminium ingots, identify the causes, and take appropriate action to prevent recurrence of the issue.
- Maintain quality records: For the purposes of quality analysis and traceability, keep track of the manufacturing details and overall state of quality for die castings and aluminium ingots.
- Continuous improvement: We continually optimise the manufacturing process and raw material quality, enhance the quality and stability of our products, and identify any issues and improvement opportunities via the study of production process and quality data.
Smelting and processing of aluminum alloys
- Preparing the raw materials: Combine the aluminium alloy’s raw materials, such as aluminium ingots, chips, scrap aluminium, etc., in a certain ratio.
Heating and melting: In order to melt the raw materials, place them in the furnace and heat them to a high temperature. Gas or electric resistance furnaces are the most common types of furnaces.
Melting temperature control: The furnace’s temperature is regulated, typically between 700 and 900 degrees Celsius, based on various aluminium alloy formulae and specifications. - Composition adjustment: To meet the necessary performance criteria, add the appropriate components to the aluminium alloy and make the necessary modifications to its composition based on the specifications of the product.
- Slag treatment: Some impurities and oxides will be formed during the melting process, necessitating slag treatment. Usually, a chemical that has the ability to absorb and purify melt impurities is used as a slagging agent.
- Degassing treatment: To enhance the quality of the aluminium alloy and eliminate gases during the smelting process, degassing treatment has to be done promptly. Several degassing techniques are often used, such as the spray and hoover procedures.
- Control of melting time: The quality of an aluminium alloy is greatly influenced by its melting time. The aluminium alloy will mix unevenly if the smelting period is too short, and it will oxidise rapidly if the smelting time is too lengthy. As a result, control over the melting time is required.
Composition adjustment and quality control of aluminum liquid
The performance and quality of the finished product are significantly impacted by the composition modification and quality control of the aluminium liquid, which are crucial steps in the aluminium die-casting process.
An essential stage in aluminium liquid quality control is composition modification. To achieve product performance criteria, aluminium liquid’s chemical composition must be controlled. The following factors are primarily involved in the composition adjustment of aluminium liquid:
- Aluminium element: With a typical percentage of more than 85%, aluminium is the primary constituent of die-cast aluminium alloy. The fluidity, shrinkage, hot cracking propensity, and mechanical characteristics of aluminium alloys are significantly influenced by aluminium elements. Based on the intended application and performance standards of the product, ascertain the aluminium element’s composition and kind.
- Alloying elements: Appropriate proportions of alloying elements, such as magnesium, zinc, copper, etc., must be added in addition to aluminium elements. The mechanical characteristics, resistance to corrosion, and thermal stability of aluminium alloys may all be enhanced by these alloying components. Choose the right alloy element type and content based on the needs of the product’s application and performance.
- Impurity elements: Iron, silicon, and other impurities may be mixed in with the aluminium alloy as it is being melted. These impurity components will have an impact on aluminium alloy quality and performance. Consequently, in order to eliminate or lower the amount of impurity components, the composition must be changed.
Chemical analysis techniques may be used to routinely detect the aluminium liquid during the composition adjustment process in order to determine its chemical composition and impurity concentration. The aluminium liquid’s composition is changed in accordance with the test findings in order to satisfy product performance specifications.
A crucial component in changing the aluminium liquid’s composition is quality control. To guarantee the quality and purity of the raw materials, it must be tightly regulated beginning with the raw materials. Simultaneously, variables like smelting temperature, duration, and charge percentage need to be managed throughout the operation to prevent the quality of the molten aluminium from declining. In order to make sure that liquid aluminum’s performance and quality fulfil specifications, it should also undergo routine testing and evaluation.
Mold design and manufacturing

Basic principles of mold design
- Functionality: The mould must be able to accomplish the anticipated moulding function and guarantee that the product’s size, form, and accuracy satisfy the specifications.
Rational structure: The mould structure should be straightforward and easy to understand, simple to produce and put together, and convenient for replacement and upkeep while in use. - Stability: To guarantee constant product quality over an extended length of time, the mould must have excellent stability and durability with repeated usage.
- Safety: In order to avoid mishaps like flashing, cracking, etc. while using the mould, operation safety should be taken into account during design.
- Economy: The manufacture and use costs of the mould should be minimised while still fulfilling functional and quality standards.
Selection and processing of mold materials
- Material selection: Choose materials with the right strength, hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability based on the demands of the product and the mold’s operating circumstances (temperature, pressure, friction, etc.).
- Heat treatment: To enhance the mechanical qualities and prolong the service life of the mould material, apply the right heat treatment, such as quenching, tempering, carburizing, etc.
- Surface treatment: To increase the mold’s resistance to corrosion and surface quality, its surface is polished, ground, plated, and given additional treatments.
Mold manufacturing process flow
- Mould design: Create drawings and design the mold’s structure based on the specifications of the product and the operating environment.
- Material preparation: Get or produce the mold’s materials, and carry out the required preprocessing and inspection.
- Processing and manufacturing: Mould pieces are produced using wire cutting, EDM, mechanical processing, and other techniques according on the specifications specified in the drawings.
- Assembly and debugging: Put the processed mould components together, troubleshoot, and test the mould to make sure it operates as it should.
- examination and acceptance: Before releasing the mould for usage, carry out a thorough examination to make sure it satisfies all design and product criteria.
Mold maintenance and care
- Frequent inspections: Perform thorough mould inspections on a frequent basis to identify and address any issues, such wear, corrosion, cracks, etc., in a timely way.
- Cleaning and upkeep: To avoid mould surface damage and deterioration of product quality, keep the mould clean and routinely remove oil and other pollutants from its surface.
- Lubrication and upkeep: To minimise wear and lengthen the mold’s lifespan, oil the mold’s moving components on a regular basis.
- Repair and replacement: To guarantee the mold’s regular functioning and the quality of the final product, promptly repair or replace mould components that are seriously worn out or damaged.
- Record management: Keep track of the mold’s use, repairs, and maintenance so that it may be managed and maintained going forward.
Aluminium die-casting process
Aluminum die casting is a process in which liquid aluminum is injected into a mold under high pressure and cooled to obtain aluminum products of the desired shape and size.
- Making liquid aluminium: To make liquid aluminium, higher quality aluminium ingots must first be melted to a molten condition and then the necessary alloying components are added. To guarantee its purity throughout this process, the aluminium liquid must go through purification procedures including degassing and slag removal.
- Choose a die-casting machine: Choose a die-casting machine that meets the specifications for die-casting goods in terms of size, shape, and precision. The two kinds of die-casting machines are hot chamber and cold chamber. Small, thin-walled objects may be produced using the former, while huge, thick-walled ones can be produced using the latter.
- Installation and adjustment of die-casting moulds: Establish the planned mould on the machine’s mobile and permanent moulds. Then, make necessary adjustments to the mold’s location and opening/closing stroke to guarantee a secure and precise fit.
- Pouring and filling: Melted aluminium enters the mould cavity via the sprue during the die-casting process. The filling effect of liquid aluminium and the final product’s quality are significantly influenced by the temperature and speed of the pour. Filling is the process by which the aluminium liquid rapidly and under high pressure fills the mould cavity; die casting is made after a brief period of solidification.
- Demoulding and cooling: Following the completion of the aluminium liquid filling, the mould cools to harden the die casting. The product’s size and complexity determine how long it takes to cool. The die-casting is removed from the mould by opening it after it achieves a certain hardness.
- Screening and quality inspection: Die-casting components must be tested for quality, including dimensions, weight, and appearance, once they are demoulded. It is necessary to filter and handle unqualified items to make sure the finished product’s quality satisfies the specifications.
Post-processing process
Trimming and removing sprues
Sprues and overflows are important features in the die-casting process that direct molten aluminium into the mould cavity. After the die casting is created, these structures are not necessary. As a result, sprue cutting and removal are crucial post-die casting processing procedures.
- Trimming: To ensure that the die casting satisfies the design specifications, cut out any surplus material around the edge using an edge trimmer or punch. Trimming neatens the die cast by getting rid of extra metal.
- Take out the sprue: This is the canal that connects the mould cavity to the gate. These connecting sections have to be taken out after die casting. Manual, mechanical, or laser cutting techniques may all be used for this operation.
Surface treatment technology
Die castings may have surface imperfections including burrs, pores, and bulges. Surface treatment is often necessary to enhance die castings’ look and functionality.
- Polishing: To eliminate surface flaws and smooth the die casting’s surface, use a polishing machine or hand polishing. Additionally, polishing may improve the metal’s appearance and texture.
- Spray coating: Die castings may have a protective coating applied to their surface using spray coating technology to increase wear and corrosion resistance, among other properties. Paint, plastic, and other materials are often sprayed.
- The technique of applying metal or non-metallic materials to die castings’ surfaces is called electroplating. Electroplating is a technique that may be used to generate a coating layer with specific qualities on the die casting surface, such as nickel or chromium plating.
Heat treatment and strengthening process
The methods of heat treatment and strengthening are essential to enhancing die casting performance even more.
- Heat treatment: The interior metallographic structure of the die casting is modified to enhance its mechanical characteristics and stability by heating and cooling it. Annealing, quenching, and other heat treatment procedures are often used.
- Process of strengthening: Using certain techniques, die castings are made harder and more resistant to wear via the process of strengthening. Die castings with surface hardening treatment, for instance, have a harder surface and better wear resistance.
Quality inspection and finished product packaging
To make sure the die-casting components fulfil the specifications, a quality inspection is required after a number of post-processing procedures.
- Quality inspection: use performance testing, dimensional measurement, visual examination, and other methods to thoroughly assess the die castings’ quality. Die castings that are deemed unqualified must be repaired or discarded.
- Final product packaging: To preserve their integrity during storage and transit, qualified die-cast components need to be packaged properly. Appropriate packing materials and techniques, such as wooden boxes, cartons, plastic bags, etc., may be chosen based on the specifications and features of the die-casting components.
Production management and optimization
creation and execution of production schedules
One crucial step in the aluminium die-casting process is the creation of production planning. It entails giving careful thought to factors including raw material availability, manufacturing capability, and market demand. The main procedures for creating and carrying out production plans are as follows:
- Market research and analysis: Gain an understanding of the competitive landscape, product development trends, and market demand via market research, which also serves as a foundation for production plan design.
- Create production plans: Using the information from market research, company strategy objectives, and available resources, create comprehensive short- and long-term production plans.
- Resource scheduling and allocation: To guarantee the manufacturing process moves along smoothly, logically distribute resources like labour, machinery, raw materials, etc. in accordance with the production plan.
- Production scheduling and execution: Work with the production plan to schedule different production links, make sure that the plan is followed, and promptly address issues that arise throughout the production process.
- manufacturing data may be tracked in real time, allowing for the quick identification and resolution of issues with the manufacturing process. Production plans can also be modified to guarantee on-time delivery.
Keeping an eye on things and making adjustments while producing
Real-time monitoring and adjustments to the manufacturing process are necessary to guarantee the stability and quality of aluminium die-casting. The following are some essential tracking and correction steps:
- Equipment status monitoring: Make sure the die-casting machines, moulds, and other pieces of equipment are in good working order by keeping an eye on their operational state in real time using equipment sensors and instruments.
- Process parameter control: Throughout the die-casting process, critical process parameters like temperature, pressure, and time are monitored and managed in real-time to guarantee the stability and precision of the parameters.
- Quality inspection: To make sure that the product quality satisfies requirements, randomly or thoroughly examine die-casting components to look for issues with size, performance, appearance, and other indications.
- Handling of unqualified products: To avoid a recurrence of the issue, examine the reasons behind unqualified die-casting components and promptly modify the manufacturing process.
- Recording and analysis: To analyse and improve the production process, record a variety of data throughout the process, including process parameters, equipment operating parameters, quality inspection findings, etc.
Management and optimisation of production costs
Cost management is essential to the manufacturing process of aluminium die casting. Here are a few ways to save costs:
- Optimise process parameters: By doing so, you may cut down on energy use and raw material waste.
- Boost production efficiency: By enhancing equipment upkeep and boosting equipment utilisation, bolster production efficiency and lower manufacturing expenses per unit of output.
- Lower the scrap rate: Lower the scrap rate by enhancing quality control, optimising manufacturing procedures, and taking other steps that will cut waste.
- Reasonable inventory management and procurement: To prevent waste and backlogs in inventory, correctly buy raw materials based on real production demands. Effective inventory management also lowers the expenses associated with inventories.
- Management of human resources: Allocating resources sensibly, enhancing worker productivity, and cutting labour expenses.
Development and innovation trends in the aluminium die-casting process
The method of die-casting aluminium is always evolving due to the progress of technology and the shifting needs of the market. The following are some potential breakthroughs and development trends:
- Utilisation of novel materials: Create novel aluminium alloy materials to enhance die castings’ mechanical characteristics and resistance to corrosion. Investigate the potential uses of additional metals in the die casting industry concurrently.
- Intelligent production: To achieve automation, informatization, and intelligence of the production process and to enhance production efficiency and product quality, introduce intelligent technologies such as industrial robots, Internet of Things, big data analysis, etc.
- Encouragement of ecologically friendly manufacturing: As environmental consciousness grows, the aluminium die-casting industry’s green growth is pushed to cut down on resource waste and contamination to the environment during production. For instance, actions like recycling garbage and using ecologically friendly release agents are taken.
- Achieving flexibility in customisation and small batch manufacturing requires developing tools and procedures that can swiftly swap out moulds, adapting to changes in market demand, and realising customisation and small batch production.
- Extend application fields: Investigate the potential uses of aluminium die-casting technology in the domains of aerospace, lightweighting cars, new energy, and other areas, and broaden the range of applications for aluminium die-casting components. To gain more precise and thorough information on innovation and development trends, please refer to relevant literature or specialists.
Safety and environmental issues
Risks to safety and precautions to take while die-casting aluminium:
The process of die-casting aluminium may include several safety risks. Corresponding preventative actions must be done in order to guarantee production safety. The following are some typical safety risks and safety measures:
- Burns from high temperatures: Burns from the high-temperature metal liquid used in the die-casting of aluminium are rather common. Wearing the proper protective gear, such as gloves and shoes, and avoiding direct contact with hot metal liquids are examples of precautions.
- Mechanical injury: Pinching, cutting, and other forms of mechanical harm may happen while a die-casting machine is in operation. Strict adherence to operating protocols, the use of gloves and adequate protective gear, and making sure that equipment safety guards are in place are examples of preventive measures.
- Gas and dust: Dangerous gases and dust may be created during the die-casting of aluminium, endangering the health of the workers. Enhanced ventilation, the use of the proper personal protective equipment, and routine environmental cleaning and monitoring are examples of preventative approaches.
- Noise and vibration: The die-casting machine will produce noise and vibration during operation, which may be detrimental to the workers’ comfort and hearing. Controlling noise sources, using silencers, doing regular hearing examinations, and giving employees a pleasant workspace are examples of preventive methods.
- Additional safety risks include those related to electrical safety, operating at heights, etc. It is necessary to take the appropriate precautions, such as routinely inspecting electrical equipment and guaranteeing the working platform’s safety.
Environmental laws and standards for disposing of waste:
In order to guarantee that the manufacturing process satisfies environmental standards, the aluminium die-casting industry must adhere to pertinent environmental rules and waste disposal criteria. The following are some typical laws pertaining to the environment and garbage disposal:
- Pollutant emission control: In order to guarantee that pollutant emissions meet criteria, aluminium die-casting firms are required by both national and municipal environmental protection rules to regulate the emission of waste gas, waste water, and solid waste.
- Waste categorization and treatment: Depending on the kind and nature of the waste, many treatment techniques are used. Sorting recyclable garbage into different categories and delivering it to certified recycling organisations for processing is necessary. Hazardous waste must be sent to certified disposal facilities, and general waste must also be treated correctly in compliance with applicable laws.
- Environmental protection facilities and equipment: To guarantee that pollutants are adequately treated during the production process, aluminium die-casting companies must be outfitted with the appropriate environmental protection facilities and equipment, such as waste water treatment facilities and exhaust gas treatment devices.
- Environmental impact assessment and acceptance: Before being used, newly constructed, remodelled, and extended aluminium die-casting projects must go through an environmental impact assessment and be approved by the environmental protection agency.
- Improvement of employee awareness and training: In order to guarantee that environmental protection regulations are properly applied throughout the production process, aluminium die-casting companies must provide their staff with environmental protection training to raise their level of awareness and sharpen their operational skills.
Green manufacturing techniques, pollution reduction, and energy conservation:
The aluminium die-casting sector may lower energy consumption, cut emissions, and increase resource utilisation efficiency by using a number of green manufacturing and energy-saving techniques. Here are a few potential actions:
- Optimise process parameters: By carefully choosing the die-casting process’s parameters, you may cut down on energy use and raw material waste. For instance, maximising mould design, managing process variables like pressure and temperature, raising die casting certification rates, and lowering scrap rates.
- Energy recycling: To cut down on energy waste, recuperate and repurpose the waste heat from the aluminium die-casting process using waste heat recovery technology. For instance, die-casting moulds are heated or preheated using waste heat from the smelting furnace.
- Employ clean energy: To lessen reliance on fossil fuels, give priority to the use of clean energy in the manufacturing process, such as solar, wind, and other forms of energy.
- Increase equipment efficiency: Through technological advancements and equipment updates, die-casting machines and other manufacturing equipment may operate more efficiently while using less energy and resources. Use energy-saving devices, such as energy-saving lighting and high-efficiency motors, as an example.
- Boost production management: By making sensible preparations for production schedules, streamlining production procedures, and taking other steps, you may cut down on the amount of energy and resources used during production. Concurrently, we will bolster environmental oversight and management throughout the manufacturing process to guarantee that contaminants are efficiently handled and emissions adhere to regulations.
- Encourage the creation of a green supply chain: Aluminium die-casting businesses may work with suppliers to encourage eco-friendly materials and green manufacturing techniques, as well as to collaboratively accomplish sustainable development objectives.
- Innovation and continual improvement: Always look for new methods and tools, enhance and optimise the manufacturing process, increase the effectiveness of resource use, and use less energy. Employees are also urged to take part in creative projects, energy-saving techniques, and emission-reduction strategies in order to collectively support the company’s sustainable growth.
sebagai kesimpulan
Aluminum die casting is a critical process that involves the selection of high-quality ingots that meet specifications and undergo strict quality control. The smelting and processing of aluminum alloys includes raw material preparation, heating and melting, adjusting melting temperature, composition adjustment, slag treatment, degassing treatment, controlling melting time, etc. Aluminum is a key material in the production of a variety of products, including molds. The process of desain cetakan involves selecting and processing materials, ensuring they meet the required specifications, and are appropriately heat treated and surface treated. Aluminum die castings undergo a variety of surface treatment techniques to enhance their appearance and functionality. Die-casting aluminum is a rapidly evolving process that continues to evolve due to technological advances and market demand. The industry is exploring new materials to enhance the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of die-casting parts. Intelligent production technology is continuously introduced to improve efficiency and product quality. The aluminum die-casting industry is also promoting eco-friendly manufacturing with the aim of reducing resource waste and environmental pollution. The industry is also exploring the application of aluminum die-casting technology in aerospace, automobile lightweighting, and new energy fields.






