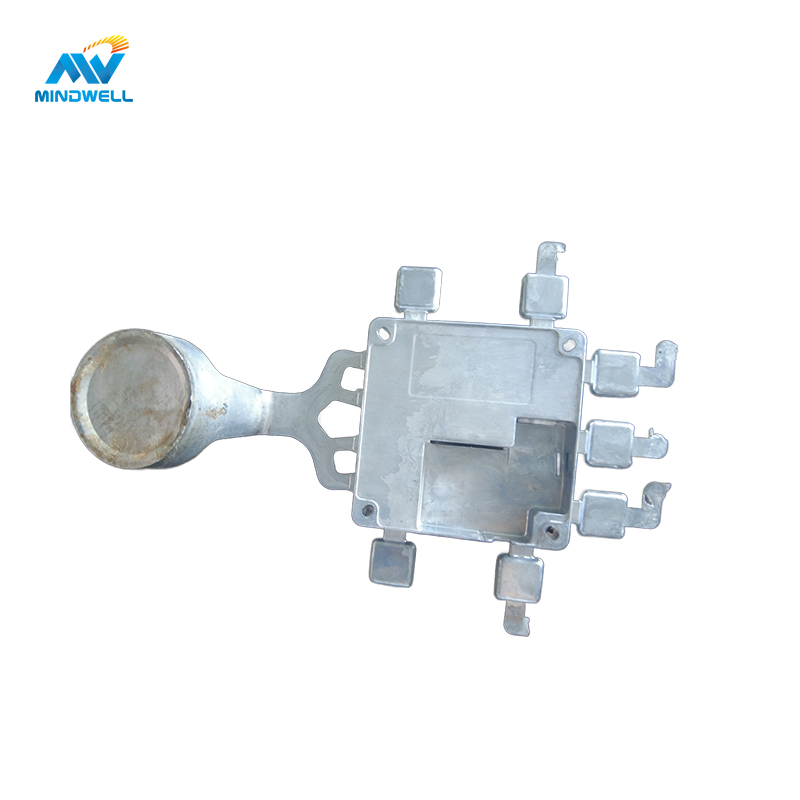
Aluminiumdruckgussteile sind Bauteile, die im Druckgussverfahren aus Aluminium hergestellt werden, wobei das Funktionsprinzip darin besteht, das Aluminium zu erhitzen, um es in einen flüssigen Zustand zu überführen. Der flüssige Aluminiumwerkstoff wird mit Hilfe eines Einspritzverfahrens in den Formhohlraum einer Sand- oder Metallform gespritzt. Der Formhohlraum kann in verschiedenen Formen und Größen gestaltet werden. Wenn der flüssige Aluminiumwerkstoff den Hohlraum füllt, nimmt er die vorgesehene Form an, was zur Herstellung von Aluminiumdruckgussteilen führt.
Aluminiumwerkstoffe lassen sich in Reinaluminium und Aluminiumlegierungen einteilen, wobei es je nach Schmelzpunkt und Härte unterschiedliche Qualitäten gibt. Druckguss ist ein Verfahren zur Herstellung von Bauteilen und lässt sich weiter untergliedern in Druckguss, Niederdruckguss, Kokillenguss und andere. Aluminiumdruckgussteile finden breite Anwendung in verschiedenen Branchen, unter anderem in der Automobil-, Elektronik-, Maschinen-, Möbel- und Motorenindustrie. In den folgenden Abschnitten geben wir eine umfassende Einführung in den Aluminiumdruckguss.
Die Entwicklungsgeschichte des Aluminiumdruckgusses

Das Druckgussverfahren lässt sich bis ins frühe 19. Jahrhundert zurückverfolgen, als Druckgussteile aus Bleizinn und Aluminiumlegierungen erstmals für Druckgeräte, Verpackungen und Drucktypen verwendet wurden. Das Verfahren hat eine über 150-jährige Geschichte. Zu Beginn des 20. Jahrhunderts begann sich die Technologie des Druckgusses von Aluminiumlegierungen zu entwickeln. Jahrhunderts begann sich die Technologie für den Druckguss von Aluminiumlegierungen zu entwickeln. 1905 wurden industrietaugliche Druckgussmaschinen eingeführt, und das Druckgießen von Bauteilen aus Aluminiumlegierungen gewann an Popularität. Aufgrund der damaligen Beschränkungen bei den Legierungsmaterialien und der Konstruktionsweise konnte der Druckguss von Aluminiumlegierungen jedoch nur eine begrenzte Anzahl einfacher Teile herstellen.
1927 entwarf der tschechische Ingenieur Josef Polak ein Säulenmodell Kältekammer Aluminiumdruckgussmaschine, die eine bedeutende Entwicklung in der Technologie darstellte. Diese Innovation brachte der Branche ein hohes Maß an Flexibilität, Kosteneffizienz und verbesserter Produktleistung. Entwurf und die Herstellung von Aluminiumdruckgussteilen. Im Jahr 1952 wurde in der ehemaligen Sowjetunion die erste Aluminium-Kaltkammer-Druckgussmaschine hergestellt, die die Herstellung von Druckgussstücken aus Aluminiumlegierungen weiter popularisierte.
Bis 1966 wurden die Grundsätze der Präzision, Geschwindigkeit und Dichte beim Aluminiumdruckguss festgelegt, und 1969 führten die Briten das gasporöse Aluminiumdruckgussverfahren mit Sauerstoffinjektion ein. Im Laufe von 150 Jahren hat sich der Aluminiumdruckguss von seinen Anfängen zu einer ausgereiften Industrie entwickelt. Sowohl die Werkstoffe als auch die Produktionstechniken haben sich ständig verbessert, und die Marktnachfrage ist gestiegen. Während des gesamten Produktionsprozesses wurden verschiedene Optimierungen vorgenommen, wie z. B. die Verfeinerung der Zusammensetzung von Aluminiumlegierungen und die richtige Einstellung der Formen, um Produktfehler zu reduzieren.
Mit dem kontinuierlichen Fortschritt verschiedener wissenschaftlicher und technologischer Entwicklungen spielt der Aluminiumdruckguss eine immer wichtigere Rolle bei der Konstruktion, Herstellung und Montage in der modernen Fertigungsindustrie. Es erhöht die Effizienz der Fertigung und verbessert gleichzeitig die Leistung der Bauteile. Da die Marktnachfrage weiter wächst, wird Aluminiumdruckguss in großem Umfang eingesetzt werden und zu einem unverzichtbaren Bestandteil der modernen industriellen Fertigungstechnologie werden.
Was ist Aluminiumdruckguss?
Aluminiumdruckguss, auch bekannt als Aluminiumdruckguss, ist eines der Produktionsverfahren für Bauteile aus Aluminiumlegierungen. Dabei wird geschmolzene Aluminiumlegierung unter hohem Druck in eine Form gespritzt und anschließend verfestigt und abgekühlt, um Formteile aus Aluminiumlegierung zu erhalten. Der Prozess des Aluminiumdruckgusses kann in mehrere Schritte unterteilt werden, darunter die Materialvorbereitung, der Entwurf der Form, die Herstellung der Form, das Schmelzen und Gießen, die Schlackenentfernung durch Vibration und die Wärmebehandlung. Der Aluminiumdruckguss weist die folgenden Merkmale auf:
- Hohe Komplexität der Produktformen, die eine hochpräzise Bearbeitung sowohl der Innen- als auch der Außenformen ermöglicht.
- Kann großformatige, hochfeste und leichte Druckgussteile herstellen.
- Kostengünstig, mit kurzen Produktionszyklen, geeignet für die Massenproduktion.
Die mit diesem Verfahren hergestellten Aluminiumdruckgusskomponenten finden breite Anwendung in Branchen wie der Automobilindustrie, der Luft- und Raumfahrt, der Telekommunikation, der Elektronik, dem Maschinenbau und dem Bauwesen.
Materialien aus Aluminiumlegierungen für Druckgussstücke
Druckgusswerkstoffe aus Aluminiumlegierungen werden hauptsächlich in drei Hauptkategorien unterteilt: Aluminium-Silizium-Legierungen, Aluminium-Silizium-Kupfer-Legierungen und Aluminium-Magnesium-Legierungen. Hier sind die chinesischen Namen und die entsprechenden englischen Übersetzungen für diese Materialien:
Aluminium-Silizium-Legierungen:
- YL102 (ADC1, A413.0, usw.)
- YL104 (ADC3, A360, usw.)
Aluminium-Silizium-Kupfer-Legierungen:
- YL112 (A380, ADC10, usw.)
- YL113 (3830)
- YL117 (B390, ADC14, ADC12, usw.)
Aluminium-Magnesium-Legierungen:
- 302 (5180, ADC5, ADC6, usw.)
In Aluminium-Silizium-Legierungen und Aluminium-Silizium-Kupfer-Legierungen sind, wie die Namen schon andeuten, die Hauptbestandteile neben Aluminium Silizium und Kupfer. Der Siliziumgehalt liegt in der Regel zwischen 6-12% und verbessert in erster Linie die Fließfähigkeit der Legierung. Der Kupfergehalt ist zweitrangig und verbessert hauptsächlich die Festigkeit und die Zugeigenschaften. Der Eisengehalt liegt in der Regel zwischen 0,7-1,2% und bietet in diesem Bereich die beste Entformungswirkung. Aufgrund ihrer Zusammensetzung sind diese Legierungen nicht anfällig für Oxidation und Färbung. Selbst mit Entsilikonisierungsverfahren ist es schwierig, den gewünschten Färbeeffekt zu erzielen. Aluminium-Magnesium-Legierungen hingegen können oxidiert und gefärbt werden, was ein wesentliches Unterscheidungsmerkmal darstellt.
Zu den spezifischen Druckgusswerkstoffen aus Aluminiumlegierungen gehören einige häufig verwendete Werkstoffe und ihre Anwendungen:
- 6061-Aluminiumlegierung: Sie bietet hohe Festigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit und gute Schweißbarkeit. Es eignet sich für Anwendungen in stark korrosiven Umgebungen, hochdichte Strukturkomponenten, Werkzeugkästen, Zubehör und mehr.
- 7075-Aluminiumlegierung: Bekannt für seine hohe Festigkeit, sein geringes Gewicht und seine leichte Bearbeitbarkeit, wird es für die Konstruktion von Flugzeugbauteilen, Raketengehäusen und Aufhängungssystemen verwendet.
- 383 Aluminium-Legierung: Hauptsächlich für Automobilkomponenten verwendet.
- 413 Aluminiumlegierung: Sie weist hervorragende Gussleistungen und Rissunterdrückungseigenschaften auf und ist daher für die Herstellung verschiedener Komponenten geeignet, darunter Teile für die Automobil- und Luft- und Raumfahrtindustrie.
- ADC12-Aluminiumlegierung: Diese Legierung bietet gute Gussleistungen und mechanische Eigenschaften und wird häufig für Anwendungen wie Automobil- und Motorradteile sowie Griffe für elektronische Produkte verwendet.
Was ist das Verfahren des Aluminiumgusses?
Der Prozess des Aluminiumgießens umfasst eine Reihe genau definierter Schritte, die für die Qualität der Gussteile und den Gesamteffekt des Gießens entscheidend sind. Lassen Sie uns diese Schritte im Detail erkunden:
- Konstruktion und Herstellung von Formen: Die Form ist ein entscheidendes Werkzeug beim Aluminiumguss, und ihre Konstruktion und Herstellung haben einen erheblichen Einfluss auf die Qualität der Gussteile. Bei der Konstruktion der Form müssen die Anforderungen an Form und Größe der Aluminiumteile, die Auswahl geeigneter Formwerkstoffe und die strukturelle Gestaltung berücksichtigt werden. Zu den gängigen Methoden der Formenherstellung gehören der manuelle Formenbau, die CNC-Bearbeitung und der 3D-Druck.
- Schmelzen von Aluminiumlegierungen: Um das Gießen zu erleichtern, muss eine Aluminiumlegierung oder reines Aluminium zu flüssigem Metall geschmolzen werden. Dies geschieht in der Regel in Elektro- oder Gasöfen. Das Aluminiummaterial wird im Ofen erhitzt, bis es sich in flüssiges Metall verwandelt. Anschließend wird das Material gehärtet, um die Festigkeit und Härte der Aluminiumteile zu erhöhen.
- Gießen:Beim Gießen wird das geschmolzene Aluminium in die Form gespritzt. Gießform. Precise control of pouring temperature and speed is crucial to preventing defects such as porosity, inclusions, and cold segregation. Maintaining the purity of the aluminum liquid is also essential to avoid impurity contamination.
- Cooling: Once the aluminum liquid is injected into the casting mold, it rapidly cools and solidifies, taking on the initial shape of the aluminum part. The cooling process requires careful control of cooling rates and temperature distribution to ensure the stability of the internal structure and size of the aluminum parts. Cooling is typically achieved using water or cooling gas.
- Demolding:Cooled aluminum parts must be carefully removed from the casting mold in a process known as demolding. Special tools and equipment such as mold vibration devices and mold unloading machines are often used for this purpose. Demolding aims to preserve the integrity and surface quality of the aluminum parts while avoiding any damage.
- Deburring:After demolding, aluminum parts often exhibit surface burrs or puncture marks. To enhance the surface quality, deburring is necessary. Deburring methods may include mechanical polishing, chemical corrosion, or sandblasting, all of which serve to eliminate surface imperfections.
- Follow-up Treatment:The final step in the aluminum casting process involves follow-up treatments, including heat treatment, surface treatment, machining, and inspection. Heat treatment enhances the organization and performance of aluminum parts, while surface treatment improves corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Machining ensures that aluminum parts meet precise size and shape requirements, and inspection guarantees quality and safety.
The aluminum casting process is intricate and rigorous, with each step demanding careful design and execution. Strict adherence to process requirements in every stage is essential to ensure the quality of aluminum parts and achieve the desired molding effect. Continuous innovation and refinement in aluminum casting processes provide valuable technical support for the advancement of the aluminum manufacturing industry.
Advantages of Aluminum Die Casting
- Mature Technology: Aluminum alloy die-casting technology is well-established, widely applied across various industries, and backed by extensive manufacturing experience, ensuring stable and reliable product quality.
- High Precision and Complexity: Aluminum alloy die-casting enables the rapid production of intricate component designs while maintaining ease of operation and achieving closed-loop process control.
- Excellent Physical Properties: Aluminum alloys offer outstanding physical properties such as ideal strength, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and excellent processability, meeting market demands.
- Good Mechanical Performance: Aluminum die-cast parts exhibit uniform composition, regular grain structure, relatively low density, high strength, good ductility, and excellent tensile and compressive strength.
- High Production Efficiency: Aluminum alloy die-casting technology significantly enhances production efficiency, reduces labor intensity, and enables large-scale production within a short timeframe.
- Thin-Wall Lightweight: Compared to other casting materials, aluminum alloy die-cast parts can have thinner production thickness, lower density, facilitating weight reduction, thin-wall design, and achieving component lightweighting and energy savings.
- Cost-Effective: Aluminum alloy die-casting technology boasts cost advantages over other manufacturing processes, being easy to use and operate, thus maintaining a competitive price advantage.
- Recyclability: Aluminum alloy materials are recyclable, contributing to environmental protection.
- Smooth Surface: Post-casting mechanical or chemical treatments yield high surface smoothness, meeting the surface requirements of self-selling products and complex assembly items.
- Customization: The manufacturing of aluminum alloy die-cast parts can be tailored to customer needs and continually refined to optimize design and production processes to the maximum extent.
- Good Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum alloy die-casting materials exhibit excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for the rapid dissipation of heat generated by electrical components or machinery.
- Precision Machining: Aluminum alloy die-casting technology enables high-precision part processing, significantly improving part accuracy and work efficiency compared to traditional machining processes.
- High Ductility: Aluminum alloy materials possess high strength, good ductility, resistance to deformation, and ease of processing into various shapes, meeting the requirements for manufacturing complex structures.
Surface Treatment Processes for Aluminum Die Casting
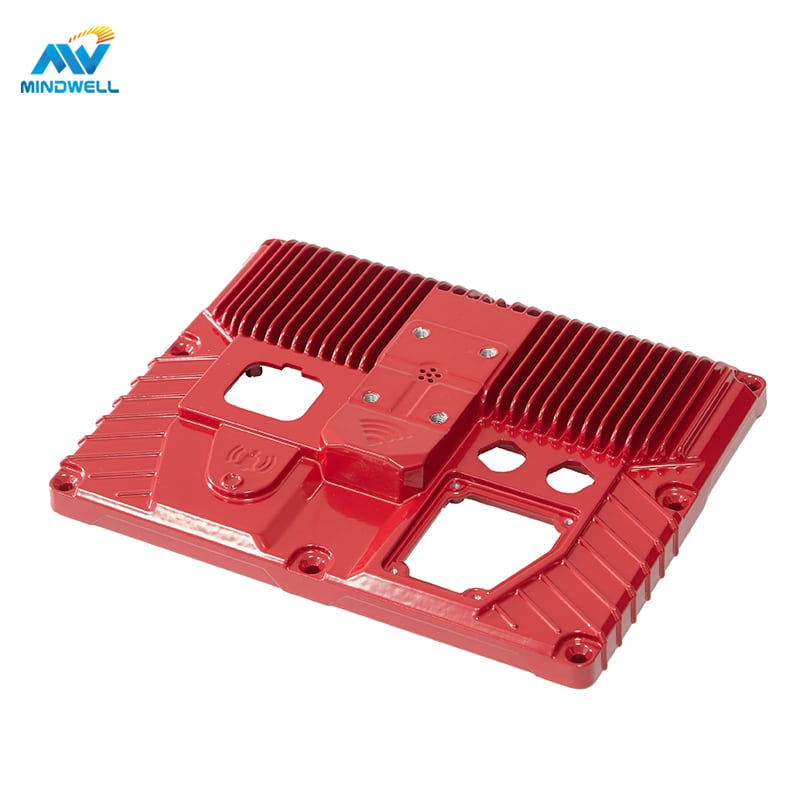

Aluminium Druckguss is a prevalent manufacturing method employed for crafting diverse aluminum alloy components. Nevertheless, aluminum alloy surfaces often necessitate treatment to enhance their resistance to corrosion, wear and tear, and their visual appeal. This article will outline several customary surface treatment processes for aluminum alloy die casting.
Electroplating Technique
Electroplating is a widely used surface treatment method that enhances the attributes of aluminum alloys by depositing a layer of metal or alloy onto their surfaces. Common electroplating procedures encompass chromium plating, nickel plating, and zinc plating. Chromium plating can augment both the corrosion resistance and the aesthetic appeal of aluminum alloys, while nickel plating enhances their durability, and zinc plating bolsters their corrosion resistance.
Coating Procedure
Coating is a straightforward and effective surface treatment process that enhances the performance of aluminum alloys by applying a coat of paint or lacquer to their surfaces. Coating offers both a pleasing aesthetic effect and protective capabilities. Common coating techniques involve spray coatings, lacquer applications, and powder coatings. Spray coatings enable aluminum alloys to exhibit various colors and textures, lacquer applications enhance their resilience against weathering, and powder coatings increase their hardness and resistance to abrasion.
Oxidation Method
Oxidation is a conventional surface treatment process for aluminum alloys, which enhances their properties by forming a layer of oxide film on the surface. Oxidation elevates corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and insulating characteristics of aluminum alloys. Common oxidation methods include anodizing and chemical oxidation. Anodizing produces a uniform and dense oxide film, whereas chemical oxidation creates an oxide film with distinct colors and textures.
Sandblasting Technique
Sandblasting is a routine surface treatment process that heightens the surface quality of aluminum alloys by propelling high-speed streams of sandblasted particles across the surface. Sandblasting eliminates oxide layers and contaminants, resulting in a smooth and even aluminum alloy surface. It also increases the surface’s roughness, enhancing lubricity and adhesion.
Polishing Process
Polishing is a frequently employed surface treatment technique that enhances the surface’s finish and flatness by mechanically polishing the aluminum alloy’s surface. Polishing imparts a mirror-like effect to the surface, enhancing its aesthetics and optical properties. Common polishing methods include mechanical polishing, electrolytic polishing, and chemical polishing.
To conclude, surface treatment processes for aluminum alloy die casting encompass electroplating, coating, oxidation, sandblasting, and polishing. These procedures serve to improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and visual appeal while enhancing the overall quality and service life of aluminum alloys. When applying these methods in practical applications, it is essential to select the appropriate surface treatment process based on specific requirements, and meticulous control of process parameters is essential to ensure the stability and consistency of the treatment outcomes.
Differences Between Aluminum Die Casting, Sand Casting, and Vacuum Die Casting
Aluminium-Druckguß
Aluminum die casting involves the use of high-pressure molten metal to cool and solidify within mold cavities, creating the desired aluminum alloy components. This process offers advantages such as high production efficiency and low cost.
The advantages of aluminum die casting include high production efficiency, low cost, and suitability for large-scale production. However, it has disadvantages, including a relatively high scrap rate, potential for post-processing requirements, and the impact of various factors on the quality of die-cast parts.
Aluminum die casting is suitable for large-scale production and scenarios where high production efficiency is required, such as in general machinery, furniture, and the electronic product industries.
Sand Casting
Sand casting, often referred to as the oldest and most versatile casting method, is capable of casting many identical parts simultaneously by sharing a single mold and reusing the same sand mold for small batch production. However, this method typically results in fewer details in the final product or a rough surface, which often necessitates post-machining, polishing, and finishing before use.
Advantages of sand casting:
- Low manufacturing cost: Sand casting generally incurs lower manufacturing costs compared to other casting methods due to lower raw material expenses and a relatively simple manufacturing process.
- High versatility: Sand casting can produce a wide range of complex-shaped castings and create various patterns and inscriptions on casting surfaces.
- High machining accuracy: Sand casting can achieve high precision in casting dimensions and surface roughness.
- Short production cycle: The production cycle for sand casting is shorter compared to other casting methods because of the simplicity of the process and short drying and hardening times.
While sand casting is a common casting method with advantages such as low manufacturing costs, high versatility, high machining accuracy, and short production cycles, its drawbacks, including average surface quality, susceptibility to sand core collapse, and extended release times, need to be considered based on practical circumstances.
Vacuum Die Casting
Vacuum die casting is a process that removes air from the mold cavity during die casting, allowing the molten metal to fill the cavity under a vacuum state, resulting in precision die-cast parts. This method effectively reduces gas entrapment, enhances the density and mechanical properties of die-cast parts.
Advantages of vacuum die casting include improving the density and mechanical properties of die-cast parts, reducing gas entrapment, lowering scrap rates, and enhancing product quality. However, it has drawbacks such as high equipment costs and relatively lower production efficiency.
Vacuum die casting is suitable for applications demanding high density and superior mechanical properties in die-cast parts, such as the automotive, aerospace, and high-end instrument industries.
In practical manufacturing, the choice of an appropriate manufacturing process should align with specific requirements, and careful attention to process parameters is vital to ensure consistent and stable treatment outcomes. As technology advances, these manufacturing processes will continue to evolve and optimize, contributing to advancements in the manufacturing industry, promising higher efficiency and quality across various fields.
Applications of Aluminum Die Casting
- Automotive Industry: Aluminum die casting is extensively used in the automotive industry for manufacturing components such as engine cylinder heads, transmission casings, clutch housings, water pump housings, carburetor housings, and steering gear housings, among others.
- Electronics and Electrical Appliances: In the field of electronics and electrical appliances, aluminum die casting is employed to produce various casings, heat sinks, and other components.
- Mechanical Tools: Aluminum die casting is used in the production of various components for mechanical tools, including handles, casings, brackets, and more.
- Other Fields: Aluminum die casting also finds applications in industries such as aerospace, telecommunications, furniture casting, gardening, lighting fixtures, household appliances, lampshades, kitchenware, furniture accessories, digital casings, craftsmanship, security product casings, LED lighting (lampshades), and some new energy industries, among others.
Schlussfolgerung
In the manufacturing industry, aluminum die casting is a versatile process that involves injecting molten aluminum into molds to create components, followed by cooling to produce high-quality parts. This method finds widespread applications in industries such as automotive, electronics, and machinery. The die-casting process encompasses critical steps, including mold design, aluminum melting, casting, cooling, demolding, deburring, and subsequent treatments. Precision and adherence to process requirements are of paramount importance for achieving success.
Advantages of aluminum die casting include well-established technology, high precision, lightweight yet robust components, and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, surface treatments like electroplating and coating can enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Aluminum die casting is known for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making it stand out among casting methods due to its precision, versatility, and product quality. As technology advances, this method continues to drive progress across various industries.






